
With the continuous advancement of modern medicine, anesthesia has evolved from a practice based on experience to one grounded in precise diagnostics and interventions. Ultrasound has become an indispensable tool for anesthesiologists, acting as an additional pair of "eyes" in clinical settings.
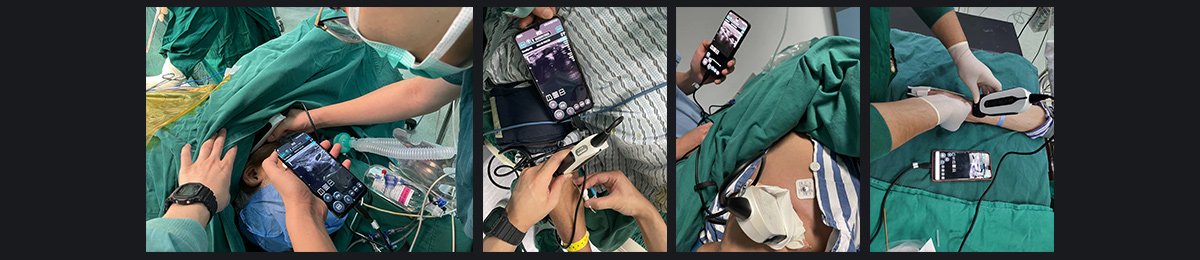
Customers Feedback
Traditional central venous catheterization relies heavily on visible anatomical landmarks and the operator's skill and experience. Challenges such as anatomical variations, obesity, pediatric patients, severe shock, weak arterial pulsation, neck deformities, and the inability to lie flat can all contribute to failed attempts. Compared to the "blind" approach, ultrasound guidance provides a more direct and reliable method.
Ultrasound-guided central venous catheterization allows for real-time visualization of the internal jugular vein, increasing the success rate of punctures and minimizing damage to surrounding tissues. This technique significantly reduces complications such as vascular injury, hematoma, pneumothorax, and catheter kinking, enhancing both the safety and efficacy of the procedure. The SonoEye handheld ultrasound, comparable in size to a smartphone but even lighter, does not occupy bedside space. Its user-friendly design allows for easy handling by physicians. The device also features puncture enhancement capabilities that improve needle visibility within tissues. Additionally, central puncture guidance lines further increase the success rate of the procedure.
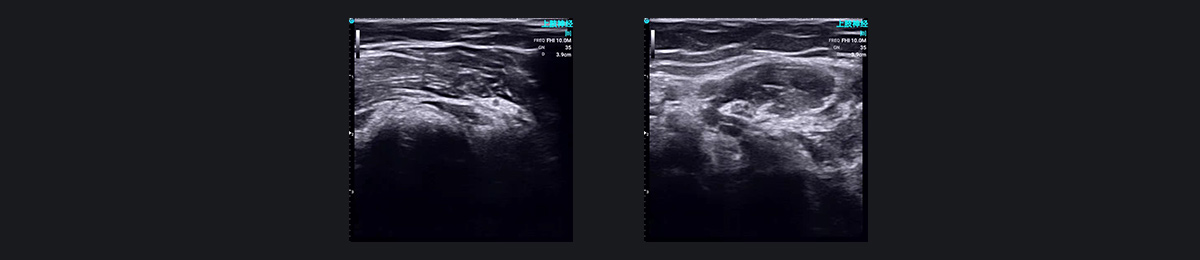
SonoEye Demo Images: Nerve Block Anesthesia
High-frequency ultrasound can clearly display peripheral nerves, enabling anesthesiologists to perform nerve blocks with greater precision and less guesswork.
Before puncture, ultrasound is used to visualize the target nerve and surrounding anatomical structures. During the procedure, real-time ultrasound imaging tracks the needle's path, avoiding injury to nerves and blood vessels, and monitors the spread of local anesthetics to ensure effective distribution. This method allows for precise nerve blocks using the minimum effective dose of local anesthetics.
Conditions such as peripheral nerve entrapment syndromes, peripheral neuropathic pain, cervical sympathetic headaches, and dizziness can be managed with ultrasound-guided local treatments or nerve block anesthesia. These techniques can also be utilized for postoperative pain management. Ultrasound-guided peripheral nerve block is accurate, minimally invasive, and highly effective, garnering widespread clinical acceptance.
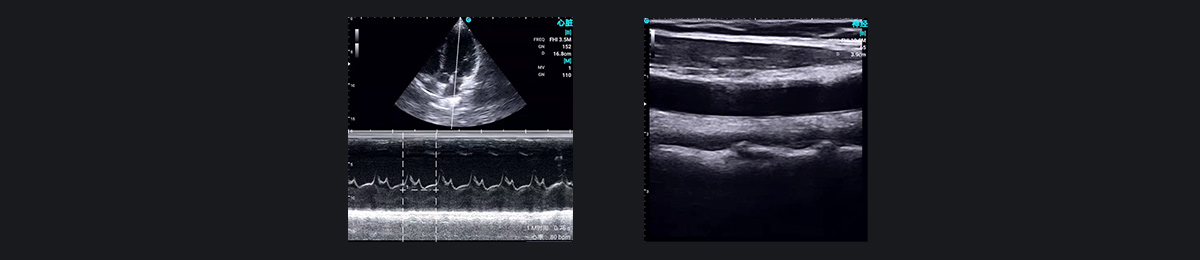
SonoEye Demo Images: Preoperative & Postoperative Care
Beyond nerve blocks, ultrasound is invaluable for assessing circulatory volume and monitoring perioperative status. Its application reduces patient harm and improves the overall experience, significantly impacting anesthesia management for cardiac surgeries and critically ill patients.
The SonoEye handheld ultrasound offers a range of probes, covering comprehensive body scans. The high-frequency linear probe provides excellent two-dimensional imaging, clearly showing the needle path, while the color mode effectively displays blood flow, helping anesthesiologists identify major blood vessels and avoid accidental punctures. The SonoEye device meets military-grade IP67 dust and water resistance standards, allowing for thorough immersion disinfection in sterile operating room environments, thereby preventing cross-infection.
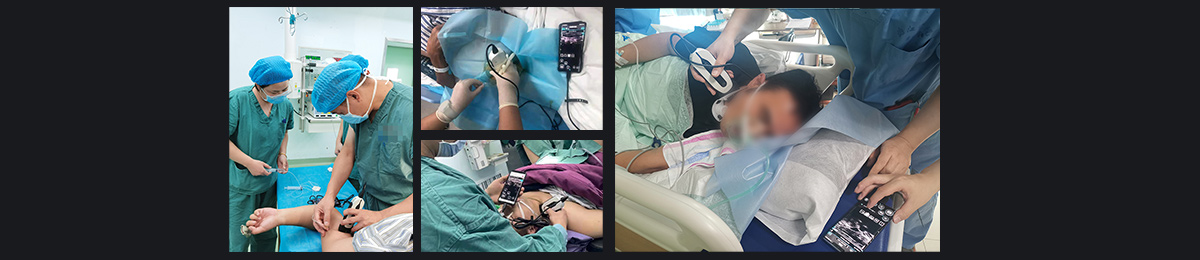
Customers Feedback
Learn more about the SonoEye handheld ultrasound by following CHISON SonoEye on major social media platforms. For pricing information, contact sonoeye@chison.com.cn.